 hide forever |
hide once
hide forever |
hide once
An MRF-Poselets Model for Detecting Highly Articulated Humans
Duc Thanh Nguyen |
Minh-Khoi Tran |
Sai-Kit Yeung |
Singapore University of Technology and Design
 |
 |
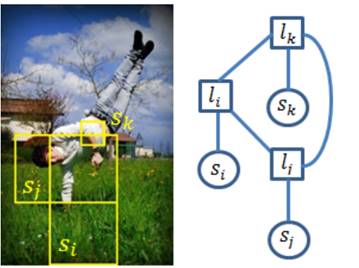 |
 |
(a) Input Image |
(b) Original Poselet detections |
(c) Remaining poselet detection after meanfield inference & corresponding MRF model
|
(d) Human Object |
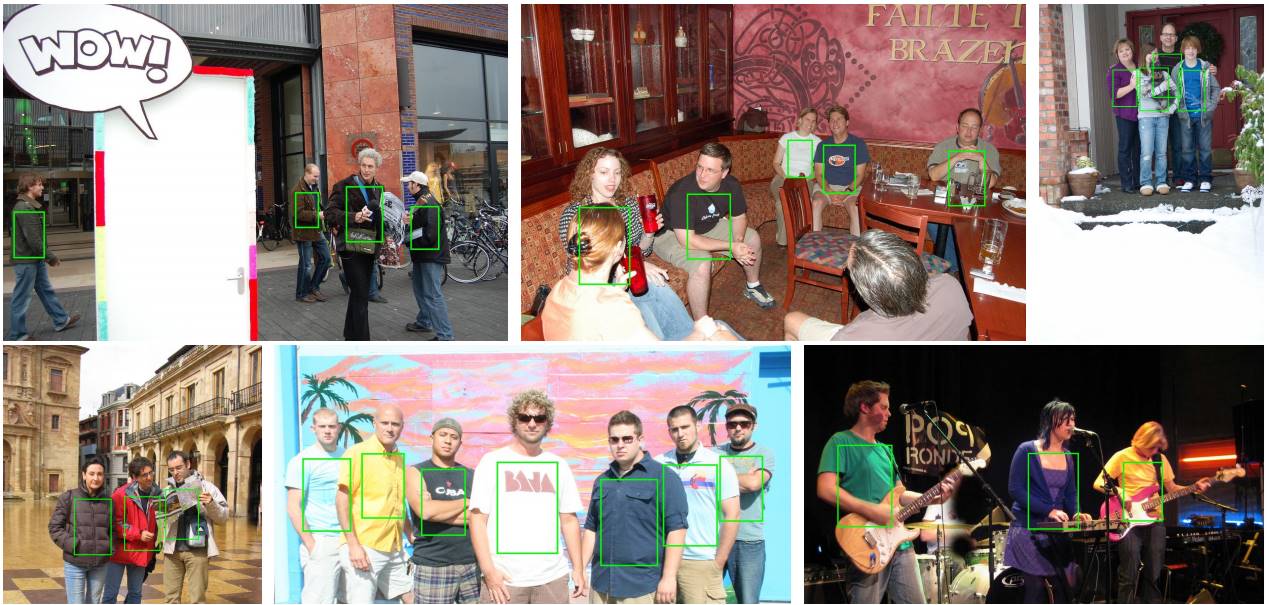
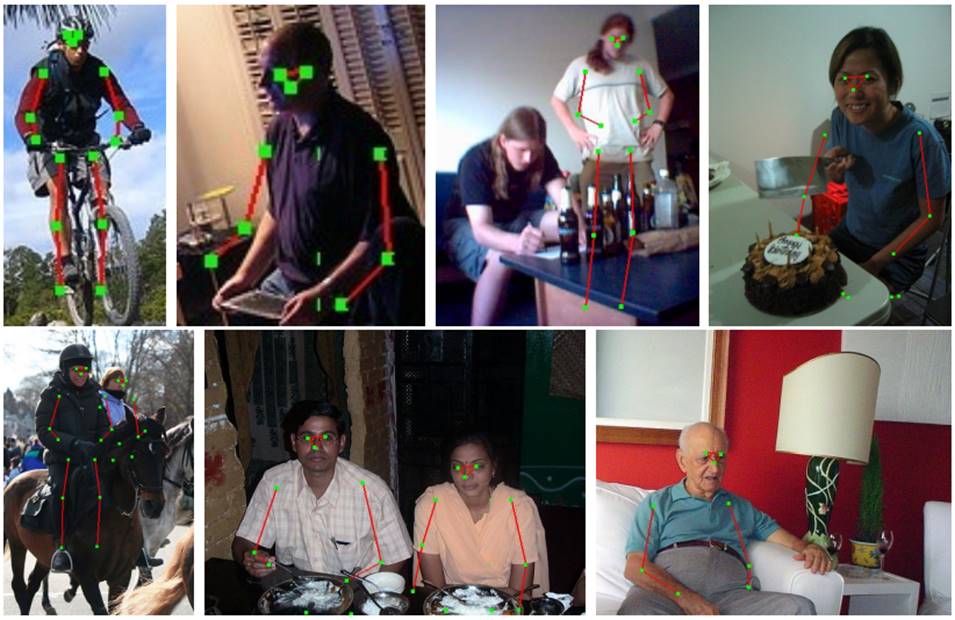
Abstract Detecting highly articulated objects such as humans is a challenging problem. This paper proposes a novel partbased model built upon poselets, a notion of parts, and Markov Random Field (MRF) for modelling the human body structure under the variation of human poses and viewpoints. The problem of human detection is then formulated as maximum a posteriori (MAP) estimation in the MRF model. Variational mean field method, a robust statistical inference, is adopted to approximate the MAP estimation. The proposed method was evaluated and compared with existing methods on different test sets including H3D and PASCAL VOC 2007-2009. Experimental results have favourbly shown the robustness of the proposed method incomparison to the state-of-the-art.
An MRF-Poselets Model for Detecting Highly Articulated Humans
Duc Thanh Nguyen,
Minh Khoi Tran,
Sai-Kit Yeung
IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2015
Paper
@INPROCEEDINGS{Nguyen_ICCV_2015,
AUTHOR = {D. T. Nguyen and M. K. Tran and S. K. Yeung},
TITLE =
{An MRF-Poselets Model for Detecting Highly Articulated Humans},
BOOKTITLE = {Proceedings of the International Conference on Computer Vision},
YEAR = {2015}
}
Sai-Kit Yeung is supported by SUTD-ZJU Collaboration Research Grant 2012 SUTDZJU/RES/03/2012, SUTDMIT International Design Center Grant IDG31300106, and Singapore MOE Academic Research Fund MOE2013-T2-1-159. Duc Thanh Nguyen and Minh-Khoi Tran are supported by Singapore MOE Academic Research Fund MOE2013-T2-1-159. We also acknowledge the support of the SUTD Digital Manufacturing and Design (DManD) Centre which is supported by the Singapore National Research Foundation.
 |
 |
 |
 |